Medical Image Segmentation (MIS) encompasses a variety of objectives, ranging from bone segmentation to organ segmentation, with each task presenting its own set of difficulties in identifying an optimal segmentation model. While the state-of-the-art nnU-Net framework has successfully automated many aspects of model configuration, it surprisingly remains constrained by fixed hyperparameters and manually designed heuristics. To address these limitations, our paper introduces Auto-nnU-Net, an AutoML framework designed specifically for the complexities of medical imaging.
Beyond Heuristics: HPO and Hierarchical NAS
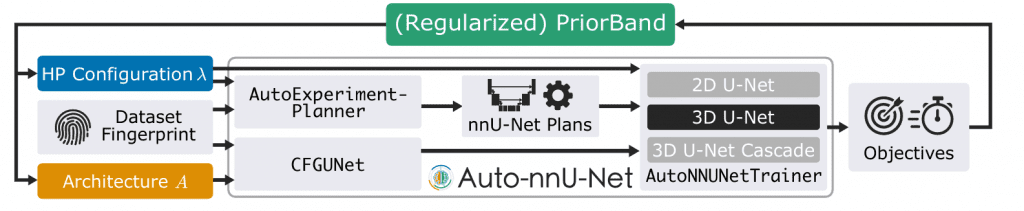
Auto-nnU-Net transforms the static nature of nnU-Net into a flexible system by integrating Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO) and Neural Architecture Search (NAS).
A standout feature is the introduction of a Hierarchical NAS (HNAS) search space. By leveraging context-free grammars (CFG), the framework can systematically refine U-Net structures. This allows for the exploration of a broader range of architectures, including diverse topological and cell-level design choices such as encoder types, normalization, and activation functions, while maintaining the core strengths of the original nnU-Net configuration.
Balancing Performance and Resources with Regularized PriorBand
Training 3D medical models is computationally demanding; the study itself required approximately 60,000 GPU hours. To address the resource constraints often faced in real-world clinical settings, the researchers proposed Regularized PriorBand.
This method enables Joint Architecture and Hyperparameter Search (JAHS) by incorporating training runtime as an explicit optimization objective alongside accuracy (1-DSC). The regularization logic is straightforward: larger or more complex models are only promoted through the search process if they contribute to a significant improvement in accuracy. This ensures the framework yields practical trade-off solutions rather than just chasing marginal gains at the cost of massive compute.
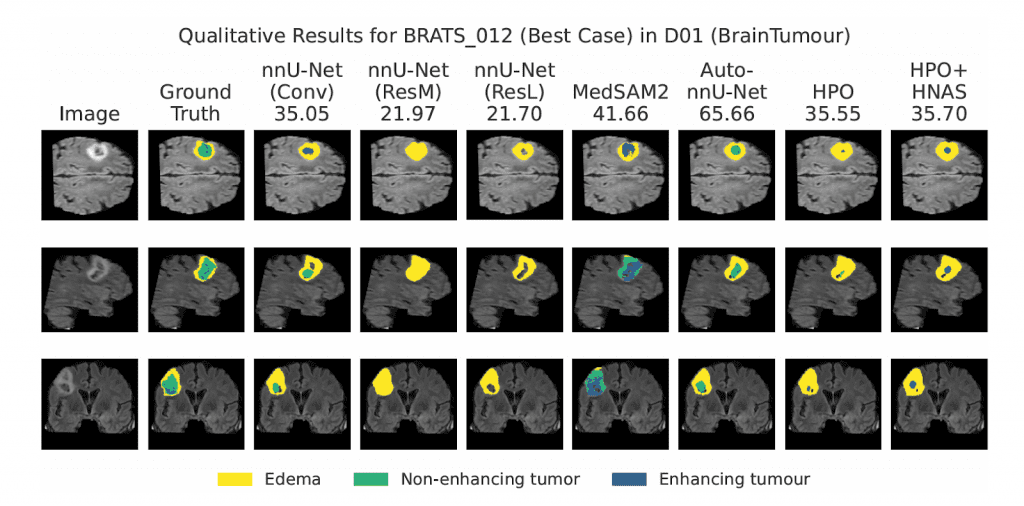
Performance across the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD)
The framework was evaluated across all ten datasets of the Medical Segmentation Decathlon, a benchmark designed to capture diversity across clinical tasks and imaging modalities. The results highlight the robustness of the AutoML approach:
- Improved Accuracy: Auto-nnU-Net substantially improved segmentation performance on 6 out of 10 datasets and remained on par with the other four.
- Superior Efficiency: In specific cases, such as the Hippocampus dataset (D04), the framework identified an optimal incumbent configuration faster than training a standard heavy “ResL” baseline.
- Outperforming Foundation Models: When compared against MedSAM2, Auto-nnU-Net achieved better results on 9 out of 10 datasets.
Conclusion
Auto-nnU-Net represents a significant step toward automated, resource-aware medical AI. Moving away from fixed heuristics and toward systematic, multi-objective optimization provides a blueprint for developing high-performing models that are feasible for the frequent retraining and localized privacy constraints required in modern medicine.
The code for Auto-nnU-Net is open-source and available on GitHub.

Comments are closed